GMV is a leading firm in the design, development, implementation and rollout of Intelligent Transportation Systems (ITS) based on IoT, mobile communications and GNSS, guaranteeing compliance with sector standards such as TRANSMODEL, GTFS, SIRI, NeTEx and CAN bus. GMV offers all-in, turnkey, ready-to-go solutions, getting involved in the complete development of the project and incorporating its own in-house hardware and software.
Our experience and continual innovative drive has brought GMV solutions to over 400 transport operators from 100 cities in countries like the United States, Spain, Malaysia, Poland, Morocco, Sweden and Mexico.
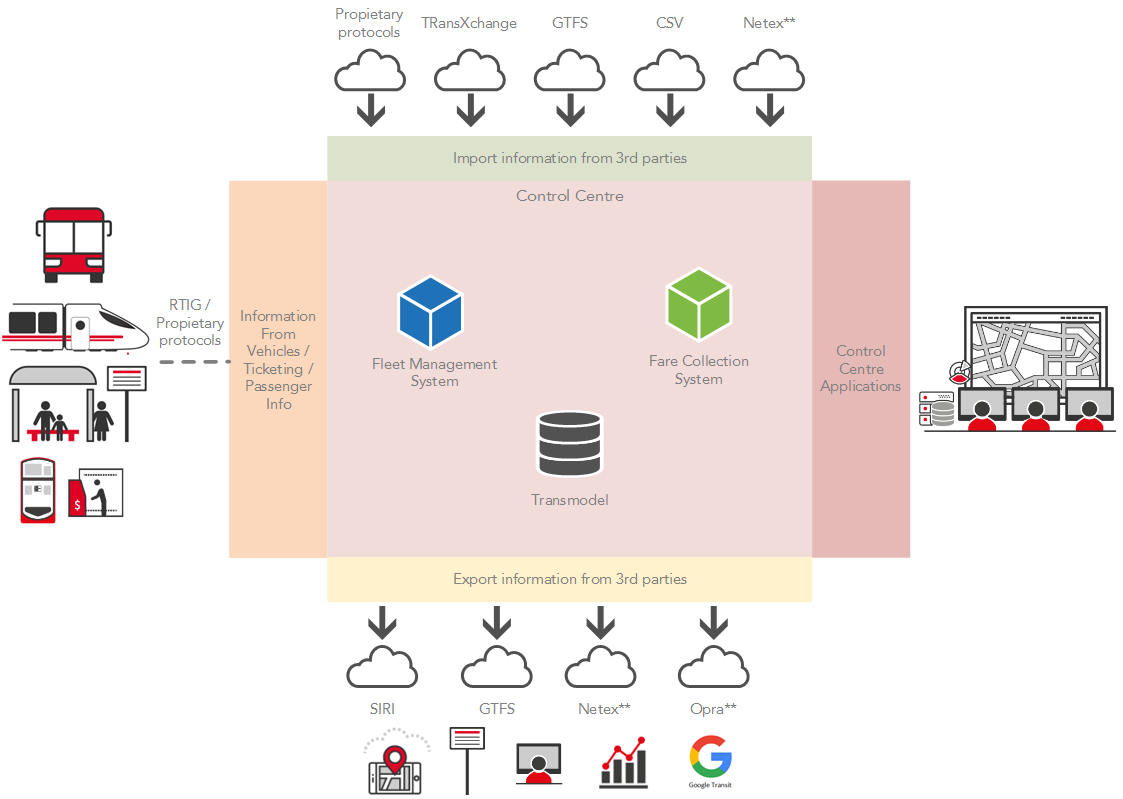
In particular GMV provides Fleet Management Systems (CAD/AVL), Fare Collection Systems, Passenger information system (on board the vehicle, at the stations, websites, mobile APPs, etc.), Service Planning Optimization tool and resource planning Optimization tool. These tools are provided both for bus and railway transportation.
 The goal of GMV ITS Solutions is to increase ridership by improving the convenience, punctuality and reliability of the transportation services. Additionally passenger information engine generates accurate and real-time information and spreads it through the channels that passengers demand today.
Return of Investment is achievable through the efficiencies and cost reduction that GMV ITS Solutions brings to Transport Providers’ operations team. Having the right information at the time when it is needed will help making the right decisions.
GMV-ITS in figures:
The goal of GMV ITS Solutions is to increase ridership by improving the convenience, punctuality and reliability of the transportation services. Additionally passenger information engine generates accurate and real-time information and spreads it through the channels that passengers demand today.
Return of Investment is achievable through the efficiencies and cost reduction that GMV ITS Solutions brings to Transport Providers’ operations team. Having the right information at the time when it is needed will help making the right decisions.
GMV-ITS in figures:
 Compliance with industry standards
GMV is compliant with the relevant industry standards to share information across systems, either supplied by GMV or third parties. This feature allows for GMV ITS Solutions integration in multimodal environments and smart mobility initiatives. GMV’s systems are based on CEN Transmodel conceptual model and some of supported exchange formats are:
Compliance with industry standards
GMV is compliant with the relevant industry standards to share information across systems, either supplied by GMV or third parties. This feature allows for GMV ITS Solutions integration in multimodal environments and smart mobility initiatives. GMV’s systems are based on CEN Transmodel conceptual model and some of supported exchange formats are:

 The goal of GMV ITS Solutions is to increase ridership by improving the convenience, punctuality and reliability of the transportation services. Additionally passenger information engine generates accurate and real-time information and spreads it through the channels that passengers demand today.
Return of Investment is achievable through the efficiencies and cost reduction that GMV ITS Solutions brings to Transport Providers’ operations team. Having the right information at the time when it is needed will help making the right decisions.
GMV-ITS in figures:
The goal of GMV ITS Solutions is to increase ridership by improving the convenience, punctuality and reliability of the transportation services. Additionally passenger information engine generates accurate and real-time information and spreads it through the channels that passengers demand today.
Return of Investment is achievable through the efficiencies and cost reduction that GMV ITS Solutions brings to Transport Providers’ operations team. Having the right information at the time when it is needed will help making the right decisions.
GMV-ITS in figures:
 Compliance with industry standards
GMV is compliant with the relevant industry standards to share information across systems, either supplied by GMV or third parties. This feature allows for GMV ITS Solutions integration in multimodal environments and smart mobility initiatives. GMV’s systems are based on CEN Transmodel conceptual model and some of supported exchange formats are:
Compliance with industry standards
GMV is compliant with the relevant industry standards to share information across systems, either supplied by GMV or third parties. This feature allows for GMV ITS Solutions integration in multimodal environments and smart mobility initiatives. GMV’s systems are based on CEN Transmodel conceptual model and some of supported exchange formats are:
- GTFS: GMV imports and exports information through GTFS files. The GTFS files exported by GMV can be used by google to publish information to the passengers (routes, schedules, fares, arrival times, etc.).
- CSV: GMV system allows to import information through predefined CSV files.
- TransXchange v2.5 is a XML based data standard orignated in the UK for the interchange of bus route and timetable information between Transport Authority, Bus Operators and passengers, and others involved in the provision of passenger information. TransXchange is based on CEN Transmodel conceptual model.
- SIRI: The Service Interface for Real Time Information or SIRI is an XML protocol to allow distributed computers to exchange real time information about public transport services and vehicles. The protocol is a CEN technical specification, developed with initial participation by France, Germany (Verband Deutscher Verkehrsunternehmen), Scandinavia, and the UK (RTIG). SIRI is based on the CEN Transmodel abstract model for public transport information, and comprises a general purpose model, and an XML schema for public transport information.
- RTIG (Digital Air Interface Protocol): RTIG is a standard air interface protocol to communicate between bus and control center. This allows having on board units supplied by different providers. RTIG is based on the CEN Transmodel
- A constant growth of integrations with different providers. For this reason it became necessary to use standards.
- The wish in the industry of independence from software and hardware suppliers.
- The need to provide information to the passengers through displays at stops, google transit, proprietary applications (Android, iOS, etc.), websites, etc.
- The need to facilitate the information exchange between different sub-systems with a common model like Transmodel and standard protocols.
- This feature allows GMV ITS Solutions integration in multimodal environments and smart mobility initiatives

Target users
- Public authorities
- Public transport operators
- Private Transport Operators
- Passengers
Implementation scope
GMV system involves over 750 Public and private Transport Operators, nearly 34.000 vehicles, more than 1,240 on stop displays, 750,000 passengers per day knowing the ETA of the next vehicle, 1,700 millions of passengers per year. There are different implementations depending on the place:- Some include all the protocols and others only a number of them.
- Some implementations exchange data with all stakeholders (Public Administrations, Operators, passengers) and others only with some of them.
- ALSA Group.
- Avanza Group.
- Prasarana Malaysia.
- Regional transport consortium of Madrid.
- Metropolitan transport authority of Barcelona.
- TMB (metropolitan transport of Barcelona).
- RENFE (Spanish National Railways).
- Government of Cyprus (Cyprus).
- Government of Galicia (Spain).
- Government of Castilla y león (Spain).
- A lot of local governments and private companies in different cities all over the world: Urban Transport of Santiago de Compostela (Spain), Urban Transport of Ourense (Spain), Urban transports of Gijon (Spain), Zaragoza Tram (Spain), Urban Transport of Valladolid (Spain), Urban Transport of Segovia (Spain), Urban Transport of Soria (Spain), Urban Transport of Caceres (Spain), Urban Transport of Mérida (Spain), Urban Transport of Toledo (Spain), Urban transport of Malaga (Spain), Urban Transport of Terrasa (Spain), Urban transport of Guadalajara (Mexico), Meknes (Morocco), Kenitra (Morocco), Kaohsiung Tram (Taiwan), Lanstrafiken Transport Company – Kronoberg (Sweden), Syarikat Prasarana Negara Berhad – Kuantan City (Malaysia), Malta Public Transport (Malta), Railway company of Mallorca Island (Spain), Warsaw Tram (Poland), Public Transport System of Szczecin city (Poland), Bus Rapid Transit of Jakarta city (Indonesia), BRT System, Ahmedabad (India), Public Transport System of the cities Gdansk, Sopot y Gdynia (Poland), etc.
