
Model for the overall Public Transport domain
What is Transmodel?
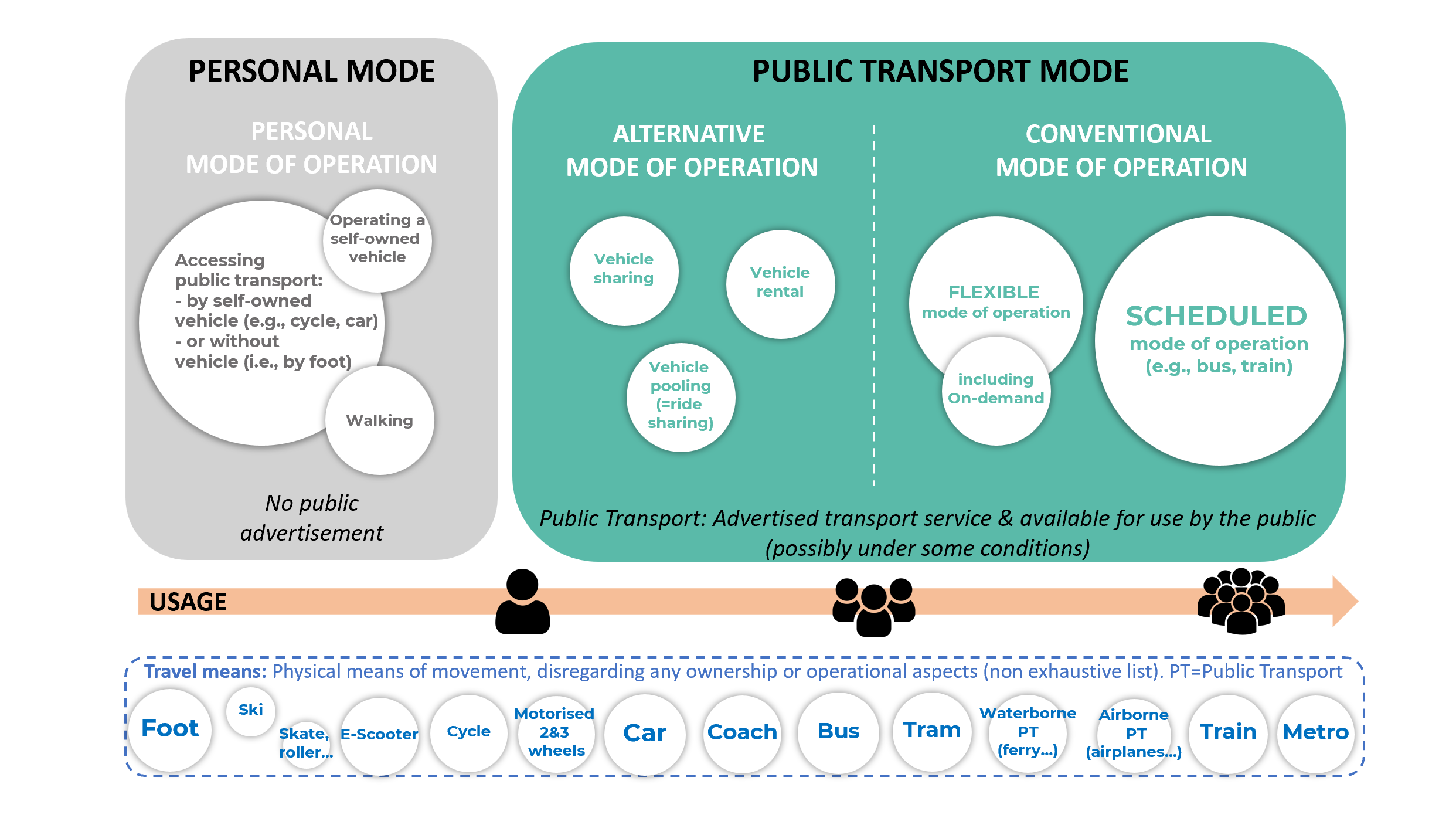
What transport modes are covered in Transmodel?
Transmodel provides an abstract model of common public transport concepts and data structures that can be used to underpin many different kinds of public transport information systems, in particular in the domain of public transport network management, timetabling, vehicle scheduling, fares management, operations monitoring and control, trip planning, driving personnel management.
Transmodel is designed for multimodality: it covers both conventional (i.e. scheduled and flexible) and alternative (e.g., vehicle sharing, taxis) modes of operations.
The figure below represents what Transmodel covers (in green) and its definition of Public Transport. By default, Transmodel does not cover any personal mode of transport.
Currently the needs of the land transport means such as bus, tramway, light-rail, metro, inland waterway vehicules (vaporreto, some local ferries), coach, long distance rail, are taken into account. For other land transport means, such as cars, (e-) cycles, (e-)scooters, etc, Transmodel considers them only in the context of vehicle sharing, vehicle pooling or vehicle rental but not within a purely personal operation. Transmodel also covers in principle other means of public transport which are not based on land transport, but waterborne (e.g. maritime cabotage) or used for air services (e.g. airplanes).
What functional areas are covered?
| Part | Functional area |
|---|---|
| 1 | Common Concepts |
| 2 | Public Transport Network |
| 3 | Timing Information and Vehicle Scheduling |
| 4 | Operations Monitoring and Control |
| 5 | Fare Management |
| 6 | Passenger Information |
| 7 | Driver Management |
| 8 | Management Information and Statistics |
| 10 | Alternative Modes |
One additional part complements this series: Part 9 – Informative documentation (CEN TR 12896-9)
Transmodel data structures are currently implemented as data exchange standards: NeTEx for planned (static) data, SIRI for real time (dynamic) data, OpRa for observed data, or are used by APIs (e.g. OJP). This means that Transmodel is implemented wherever NeTEx, SIRI, OJP, OpRA are implemented. The countries listed below have communicated implementation examples of Transmodel. To be noted that a number of European countries under the obligation of the European Delegated Regulation (EU) 2024/490 (MMTIS) (updating the DR EU 2017/1926) which have implemented National Access Points provide their Multimodal Travel Information using Transmodel-based formats.
